Woolford 2006: Lexical case, Inherent case
2021. 3. 2. 11:18ㆍlinguistics
반응형
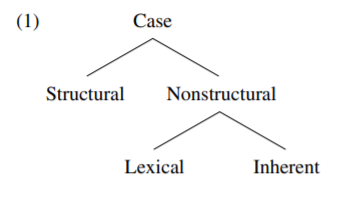
Case
-
Structural case
-
Non-structural case
2.1. Inherent case
2.2. Lexical case
1과 2 구분: A-movement
- A-movement 이후에도 case 유지되면 non-structural, 유지되지 않으면 structural
Inherent case: external argument/shifted DP goal, vP에게 격 받음
Lexical case: internal argument (e.g. theme), lexical head(V,P)에게 격 받음
- complementary distribution
vP phase에서 theta marking, non-structural case licensing
→ 이때 theta 받았는데 격 없으면 movement
→ 이후 structural case licensing (theta와 상관 없음)
Structural vs Non-structural case
-
Case Preservation under A-Movement
1.1 Passive
- passive로 바꿔도 dative 보존되는가?
- <반박> 예시로 든 독일어의 dative는 passive 변화 겪지 않음
- <문제> 일본어 transitive를 passive로 바꿔 intransitive 되었더니 dative 사라짐. 이걸 보면 structural case처럼 보임. 그러나 일본어 intransitive에선 dative subject 아예 불가능
- <해결> 일본어 ditransitive를 passive로 바꿔 transitive 되니 dative 그대로 유지. 따라서 non-structural case
- passive로 바꿔도 ergative 보존되는가? ↔ 수동문에선 ergative 사라져서 알 수 없음
1.2. Raising
- raising은 ergative도 test 가능
- raising해도 ergative 보존되는가? 보존되면 non-structural case
- passive로 바꿔도 dative 보존되는가?
-
Non-nominative subjects of tensed clauses
- 원래 주격이 license되는 자리에 주격이 아닌 격이 있으면 non-structural case
- Priority: non-structural case > nominative > other structural case
- vP phase에서 non-structural case 받았는데 이동하다 보니 주격 받을 수 있는 자리로 간 경우, T는 nom을 줘야 하니 받긴 받아야 함. 그러나 non-structural case가 더 우세해서 nominative는 소리 안 남
1. Allowing nominative objects
- 주어가 non-structural case여야 nominative object 허용 가능
↔ 주어가 어떤 격을 가지든, 주어가 존재하기만 하면 아예 nominative object 허용하지 않는 언어도 있어 주의 필요
2. Theta-relatedness
- dative = goal, ergative = agent 이렇게 일대일 대응 불가능
- dative가 goal 외에 다른 theta-role: experiencer, theme
- goal이 dative 외에 다른 case: genitive
- ergative가 agent 외에 다른 theta-role: causer, instrument
3. Regularity
- structural vs non-structural 구분엔 바람직하지 않음
- lexical (irregular) vs structural + inherent case (regular) 구분은 가능
반응형
'linguistics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Binding Theory (0) | 2021.03.03 |
|---|---|
| Yoon 2015: Double Nominative and Double Accusative (0) | 2021.03.03 |
| Saito 2012: Japanese Right Periphery (0) | 2021.03.02 |
| Rizzi 2013: Cartography of the left periphery (0) | 2021.03.02 |
| Larson 1987: Double Object Construction (0) | 2021.03.02 |