2021. 3. 21. 12:11ㆍlinguistics
Irish English에선 Standard English가 허용하지 않는 all-stranding을 허용한다
- What all did you get t for Christmas?
- Irish, Standard English 모두 허용
- What did you get all for Christmas?
- Irish English만 허용
- I don't remember what I said all.
- embedded question에서도 위와 같은 all-stranding 가능
⇒ wh-quantifier float
quantifier float과 wh-quantifier float의 유사점
- (차이) quantifier: A position / wh-quantifier: A' position
- A: occupied by an argument / A-bar: not occupied by an argument

- prosodic characteristics
- optimal when all can be incorporated into a preceding head, preferably a verb
Stranding under Long Wh-Movement
- all은 wh-movement가 시작된 곳 또는 거쳐 가는 곳에 있어야 함
- 이는 what뿐만 아니라 다른 wh-pronoun에도, finite뿐만 아니라 infinite clause에도 똑같이 적용됨
- 하지만 all이 original position (wh-movement가 orginate한 position)에 있으면 dispreference
- original position: What did he say (that) he wanted all?
- intermediate position: What did he say all (that) he wanted t?
- final position: What all did he say (that) he wanted t?

- all은 CP의 specifier 자리로 이동
- tell은 DP, CP complement 가짐. stranding all은 DP의 오른쪽, C의 왼쪽에만 올 수 있음
- (14b)와 (14d) 구조는 같지만, phonological weight이 다름. (14b)의 DP: him VS (14d)의 DP: his friends/Mickey
- successive-cyclic character of long wh-movement

Stranding under Short Wh-Movement
- clause-bounded wh-movement
- all appears inside VP
- object position: Who did he tell all he was going to resign?
- further right: *Who did he tell he was going to resign all?
- right of adjuncts: *What did she buy yesterday all?
→ 비문인 경우는 wh-movement가 지나가는 자리가 아니라서 비문?
- PP complement 필요한 동사의 경우
- wh가 지나가지 않는 자리: *Who did you talk all to?
- prepositional object: ?Who did you talk to all (at the party)?
- verb + another complement + P + all인 경우 ungramaticality 더 심함: ?Who did you give tea to all?
- prosodically substantial preposition의 object인 경우 ungramaticality 더 심함: ?*Who were you sitting beside all?
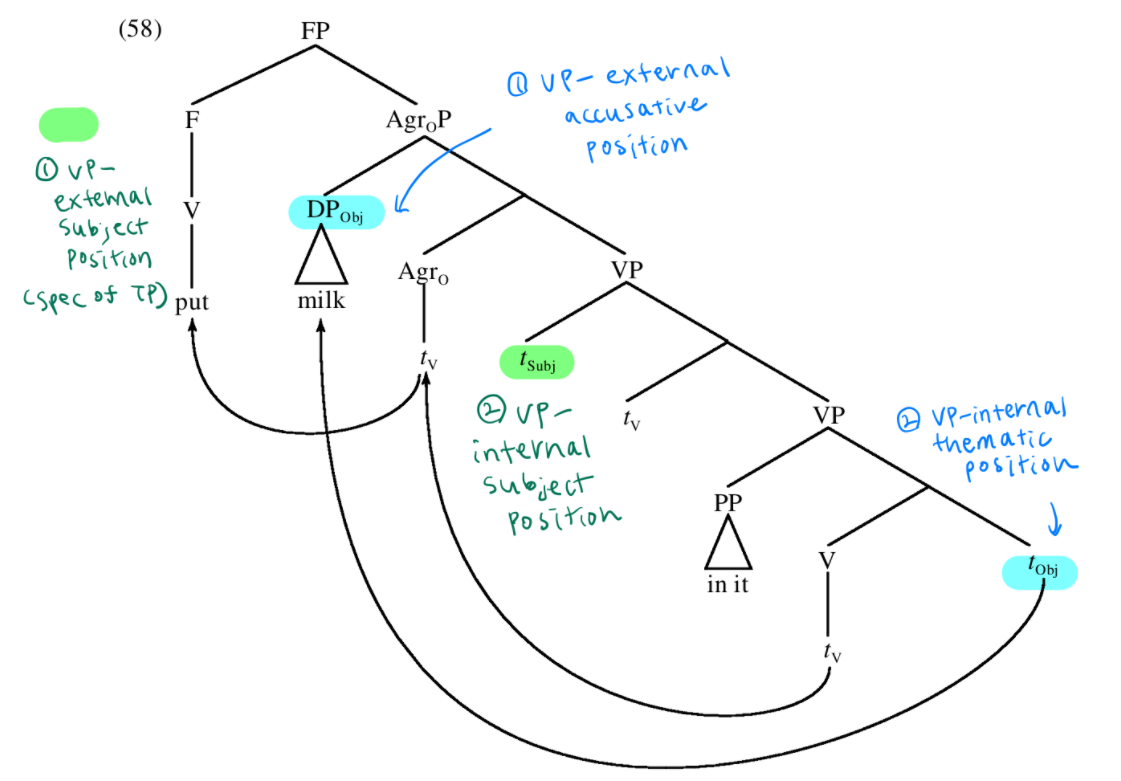
The Internal Architecture of VP
- Object Positions
(1) canonical object
- What did you put all in the drawer yesterday?
(2) right of other complement & left of adjunct
- ?What did you put in the drawer all yesterday?
(3) right of adjunct
- *What did you put in the drawer yesterday all?
→ (2)는 prosodic requirement가 ideal은 아니지만, syntactically 문제는 없음 ∴ intermediate status
syntactically
(1), (2): well-formed
(3): ill-formed
prosodically
(1): optimal
(2), (3): non-optimal
two object positions
(1) immediate postverbal position (2) right of PP complement (+ left of adjuncts)
→ ECM을 통해 알게 된 정보 (overt object shift, overt verb raising) 고려해보면,
(1) leftmost: immediate postverbal position
- VP-external accusative position (AgrO)
- What did you put all in the drawer?
(2) rightmost: position where object originates
- VP-internal thematic position
- ?What did you put in the drawer all?
→ direct object는 PP complement의 오른쪽(lower)에서 originate
- ?She told [stories about each other]_j to the children t_j.
2. Exceptional-Case-Marking (ECM) Constructions
- ECM subject: raised to accusative position (matrix VP)
- The prosecutors proved absolutely nobody to be guilty during any of the trials
not ECM (for complement)
- Who did you arrange all for your mother to meet at the party?
- all이 specifier of CP에 stranded
- *Who did you arrange for your mother all to meet at the party?
- your mother: specifier of IP / to: head of IP → 그 사이에 자리 없는데 all이 있어서 비문
- Q. 여기서 your mother은 for한테 격을 받나?
ECM
- Who did you want your mother all to meet at the party?
- all: specifier of CP (wh-movement가 지나간 자리)
- DP your mother가 all보다 왼쪽에 있는 것은 DP가 raising to accusative position 했기 때문
- *Who did you want all your mother to meet at the party?
→ not ECM과 비교해보면 반대의 패턴
- not ECM에선 all이 your mother보다 앞에 있어야 정문이었지만, ECM에선 all이 your mother보다 뒤에 있어야 정문
[결론] overt object shift, overt verb raising
3. Subjects
- unaccusative, unergative, passive predicate의 경우에도 all stranding in the postverbal position 가능
- What happened all at the party?
- Who was fighting all at the party?
→ subject position이 verb의 오른쪽에 있나? 그래야 wh-movement하면서 거쳐온 자리라 정문이 됨
- subject position: left specifier in VP
- overt object shift, raising of V: to outside VP
- stranding all: in VP-internal subject position
- Who all built this house?
- *Who built all this house?
- ?Who built this house all?
- 이 문장이 정문이 될 수 있는 조건 2가지
- ?Who changed their mind all?
- Who read it all this morning?
[stranded subject all - PP complements] 순서가 일반적임
- *Who was arguing with the boys all last night?
- Who was arguing all with the boys last night?
A-bar movement, A-movement, and Quantifier Float
movement analysis
*They have gone all to bed
*They were arrested all last night
*They froze all during the winter
*They were spoken to all after class
→ 비문인데, movement analysis에 따르면 정문으로 분석함
→ 이를 비문으로 설명하기 위한 restriction 필요
all-stranding in the postverbal subject position
- Who was throwing stones all around here?
- *They were throwing stones all around here
- 만약 who가 they랑 똑같이 spec TP 거쳐갔다면 똑같이 비문이어야 하는데, 얘는 정문임. 따라서 TP spec 거치지 않고 CP spec으로 바로 갔다는 걸 알 수 있음
- TP의 specifier 거치지 않으면 EPP 어떻게 충족?
- movement-inducing feature: "strong"
- TP의 spec은 A-position (argument) / CP의 spec은 A' position
- → who는 (they와 달리) VP-internal subject position에서 바로 CP의 specifier로 이동 (TP의 specifier 거치지 않음)
interrogative pronoun: wh-feature 있어서 all의 specifier로 이동함 → head("who all")가 wh-feature 갖게 됨 → A' position이 됨 (따라서 이 position에서 A position으로 이동 불가능)

satisfaction of the features of T
- entire subject (who all) → movement is unproblematical (from A to A position) → spec TP로 이동 후, C[+wh] 도입되면 spec CP로 다시 이동
- Who all was throwing stones in G. Square?
- only specifier of subject (who) → movement is problematical (improper movement from A' to A position) → 그래서 이동 못하고 있다가(movement가 불가능한 경우, movement 없이 feature satisfaction 가능), 다음에 C가 도입되면 who는 C의 specifier로 이동함 (A' movement)
- Who was throwing stones all in G. Square?
출처: semantics.uchicago.edu/kennedy/classes/w06/readings/mccloskey00.pdf
'linguistics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자연어처리와 언어학 지식 (0) | 2021.10.07 |
|---|---|
| Saito 2007: East Asian Argument Ellipsis (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| Han 2020: Null Object in Korean (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| Baker 1989: Passive Arguments (0) | 2021.03.21 |
| Han 2012: Semantic binding of '자기' (0) | 2021.03.03 |